-
 Gaming Computer
1 ×
$940.00
Gaming Computer
1 ×
$940.00
-
 Smartphone Vivo V9
1 ×
$899.00
Smartphone Vivo V9
1 ×
$899.00
-
 SanDisk Flash Drive
1 ×
$756.00
SanDisk Flash Drive
1 ×
$756.00
-
 Smart Power Bank
1 ×
$723.00
Smart Power Bank
1 ×
$723.00
-
 Apple Smartwatch
1 ×
$1080.00
Apple Smartwatch
1 ×
$1080.00
Subtotal: $4398.00



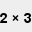 By Themeholy
By Themeholy